| dc.contributor.author | Dejeux, Emelyne | en_US |
| dc.contributor.author | Rønneberg, Jo A. | en_US |
| dc.contributor.author | Solvang, Hiroko Kato | en_US |
| dc.contributor.author | Bukholm, Ida Rashida Khan | en_US |
| dc.contributor.author | Geisler, Stephanie | en_US |
| dc.contributor.author | Aas, Turid | en_US |
| dc.contributor.author | Gut, Ivo G. | en_US |
| dc.contributor.author | Børresen-Dale, Anne-Lise | en_US |
| dc.contributor.author | Lønning, Per Eystein | en_US |
| dc.contributor.author | Kristensen, Vessela N. | en_US |
| dc.contributor.author | Tost, Jörg | en_US |
| dc.date.accessioned | 2011-01-05T10:11:46Z | |
| dc.date.available | 2011-01-05T10:11:46Z | |
| dc.date.issued | 2010-03-25 | eng |
| dc.Published | Molecular Cancer 2010, 9:68 | en |
| dc.identifier.issn | 1476-4598 | |
| dc.identifier.uri | https://hdl.handle.net/1956/4371 | |
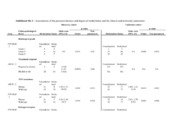
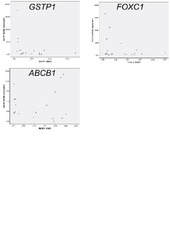
| dc.description.abstract | Background: Breast cancer is the most frequent cancer in women and consists of a heterogeneous collection of diseases with distinct histopathological, genetic and epigenetic characteristics. In this study, we aimed to identify DNA methylation based biomarkers to distinguish patients with locally advanced breast cancer who may benefit from neoadjuvant doxorubicin treatment. Results: We investigated quantitatively the methylation patterns in the promoter regions of 14 genes (ABCB1, ATM, BRCA1, CDH3, CDKN2A, CXCR4, ESR1, FBXW7, FOXC1, GSTP1, IGF2, HMLH1, PPP2R2B, and PTEN) in 75 well-described pre-treatment samples from locally advanced breast cancer and correlated the results to the available clinical and molecular parameters. Six normal breast tissues were used as controls and 163 unselected breast cancer cases were used to validate associations with histopathological and clinical parameters. Aberrant methylation was detected in 9 out of the 14 genes including the discovery of methylation at the FOXC1 promoter. Absence of methylation at the ABCB1 promoter correlated with progressive disease during doxorubicin treatment. Most importantly, the DNA methylation status at the promoters of GSTP1, FOXC1 and ABCB1 correlated with survival, whereby the combination of methylated genes improved the subdivision with respect to the survival of the patients. In multivariate analysis GSTP1 and FOXC1 methylation status proved to be independent prognostic markers associated with survival. Conclusions: Quantitative DNA methylation profiling is a powerful tool to identify molecular changes associated with specific phenotypes. Methylation at the ABCB1 or GSTP1 promoter improved overall survival probably due to prolonged availability and activity of the drug in the cell while FOXC1 methylation might be a protective factor against tumour invasiveness. FOXC1 proved to be general prognostic factor, while ABCB1 and GSTP1 might be predictive factors for the response to and efficacy of doxorubicin treatment. Pharmacoepigenetic effects such as the reported associations in this study provide molecular explanations for differential responses to chemotherapy and it might prove valuable to take the methylation status of selected genes into account for patient management and treatment decisions. | en_US |
| dc.language.iso | eng | eng |
| dc.publisher | BioMed Central | eng |
| dc.rights | Attribution CC BY | eng |
| dc.rights.uri | http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0 | eng |
| dc.title | DNA methylation profiling in doxorubicin treated primary locally advanced breast tumours identifies novel genes associated with survival and treatment response | en_US |
| dc.type | Peer reviewed | |
| dc.type | Journal article | |
| dc.description.version | publishedVersion | en_US |
| dc.rights.holder | Dejeux et al | |
| dc.rights.holder | Copyright 2010 Dejeux et al; licensee BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. | |
| dc.identifier.doi | https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-4598-9-68 | |
| dc.identifier.cristin | 340028 | |
| dc.subject.nsi | VDP::Medisinske Fag: 700::Basale medisinske, odontologiske og veterinærmedisinske fag: 710::Medisinsk genetikk: 714 | nob |