| dc.contributor.author | Bizuayehu, Teshome | en_US |
| dc.contributor.author | Lanes, Carlos Fredrico Ceccon | en_US |
| dc.contributor.author | Furmanek, Tomasz | en_US |
| dc.contributor.author | Karlsen, Bård Ove | en_US |
| dc.contributor.author | Fernandes, Jorge | en_US |
| dc.contributor.author | Johansen, Steinar Daae | en_US |
| dc.contributor.author | Babiak, Igor | en_US |
| dc.date.accessioned | 2013-03-22T09:43:23Z | |
| dc.date.available | 2013-03-22T09:43:23Z | |
| dc.date.issued | 2012-01-10 | eng |
| dc.Published | BMC Genomics 13:11 | eng |
| dc.identifier.issn | 1471-2164 | |
| dc.identifier.uri | https://hdl.handle.net/1956/6447 | |
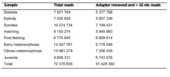
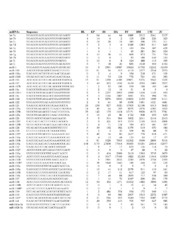
| dc.description.abstract | Background: MicroRNAs (miRNAs) play a major role in animal ontogenesis. Size variants of miRNAs, isomiRs, are observed along with the main miRNA types, but their origin and possible biological role are uncovered yet. Developmental profiles of miRNAs have been reported in few fish species only and, to our knowledge, differential expressions of isomiRs have not yet been shown during fish development. Atlantic halibut, Hippoglossus hippoglossus L., undergoes dramatic metamorphosis during early development from symmetrical pelagic larval stage to unsymmetrical flatfish. No data exist on role of miRNAs in halibut metamorphosis. Results: miRNA profiling using SOLiD deep sequencing technology revealed a total of 199 conserved, one novel antisense, and one miRNA* mature form. Digital expression profiles of selected miRNAs were validated using reverse transcription quantitative PCR. We found developmental transition-specific miRNA expression. Expression of some miRNA* exceeded the guide strand miRNA. We revealed that nucleotide truncations and/or additions at the 3’ end of mature miRNAs resulted in size variants showing differential expression patterns during the development in a number of miRNA families. We confirmed the presence of isomiRs by cloning and Sanger sequencing. Also, we found inverse relationship between expression levels of sense/antisense miRNAs during halibut development. Conclusion: Developmental transitions during early development of Atlantic halibut are associated with expression of certain miRNA types. IsomiRs are abundant and often show differential expression during the development. | en_US |
| dc.language.iso | eng | eng |
| dc.publisher | BioMed Central | eng |
| dc.rights | Attribution CC BY | eng |
| dc.rights.uri | http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0/ | eng |
| dc.title | Differential expression patterns of conserved miRNAs and isomiRs during Atlantic halibut development | en_US |
| dc.type | Peer reviewed | |
| dc.type | Journal article | |
| dc.description.version | publishedVersion | en_US |
| dc.rights.holder | Copyright 2012 Bizuayehu et al; licensee BioMed Central. | |
| dc.identifier.doi | https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-13-11 | |
| dc.identifier.cristin | 926809 | |
| dc.source.journal | BMC Genomics | |
| dc.source.40 | 13 | |
| dc.source.14 | 11 | |