| dc.contributor.author | Isaksen, Kjetil | en_US |
| dc.contributor.author | Halvorsen, Bente | en_US |
| dc.contributor.author | Munk, Peter Scott | en_US |
| dc.contributor.author | Aukrust, Pål | en_US |
| dc.contributor.author | Larsen, Alf Inge | en_US |
| dc.date.accessioned | 2020-06-19T08:53:45Z | |
| dc.date.available | 2020-06-19T08:53:45Z | |
| dc.date.issued | 2019 | |
| dc.Published | Isaksen K, Halvorsen BE, Munk PS, Aukrust P, Larsen AI. Effects of interval training on inflammatory biomarkers in patients with ischemic heart failure. Scandinavian Cardiovascular Journal. 2019;53(4):213-219 | eng |
| dc.identifier.issn | 1401-7431 | |
| dc.identifier.issn | 1651-2006 | |
| dc.identifier.uri | https://hdl.handle.net/1956/22762 | |
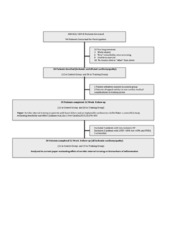
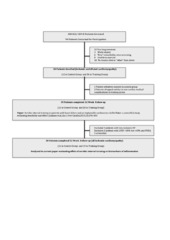
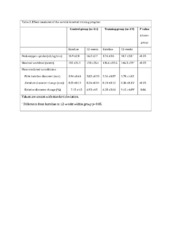
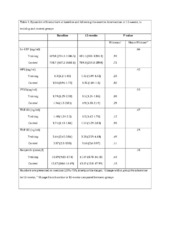
| dc.description.abstract | Objectives. Exercise training has been proposed to have anti-inflammatory effects. We examined whether aerobic interval training (AIT) can attenuate the inflammatory response in ischemic heart failure (HF) as measured by serum biomarkers representing a broad spectrum of activated inflammatory pathways. Design. We conducted a controlled prospective trial recruiting 30 patients (19 in the AIT group and 11 in the control group) with ischemic HF and an implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD). This study is a sub study of the previously reported “Aerobic interval training in patients with heart failure and an ICD” (Eur J Prev Cardiol. 22 March 2015; 22:296–303). Patients in the AIT group exercised for 12-weeks completing a total of 36 AIT sessions. We analyzed serum levels of C-reactive protein, pentraxin-3, osteoprotegerin, brain natriuretic peptide, neopterin, and soluble tumor necrois factor type 1 and 2, all known to predict an adverse outcome in HF, at baseline and following the 12-week AIT intervention. Results. The AIT group significantly increased peak oxygen uptake and improved endothelial function compared to the sedentary control group. No statistically significant changes in serum levels of the biomarkers were detected from baseline following the AIT intervention and, there were no significant differences in changes of these mediators between the AIT and the control group. Conclusions. A 12-week AIT intervention, although improving exercise capacity and endothelial function, did not attenuate serum inflammatory biomarkers in stable ischemic HF patients with an ICD on optimal medical therapy. | en_US |
| dc.language.iso | eng | eng |
| dc.publisher | Taylor & Francis | eng |
| dc.title | Effects of interval training on inflammatory biomarkers in patients with ischemic heart failure | en_US |
| dc.type | Peer reviewed | |
| dc.type | Journal article | |
| dc.date.updated | 2020-02-06T08:50:50Z | |
| dc.description.version | acceptedVersion | en_US |
| dc.rights.holder | Copyright 2019 Informa UK Limited, trading as Taylor & Francis Group | |
| dc.identifier.doi | https://doi.org/10.1080/14017431.2019.1629004 | |
| dc.identifier.cristin | 1717446 | |
| dc.source.journal | Scandinavian Cardiovascular Journal | |