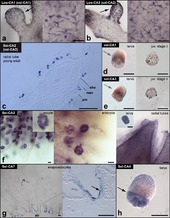
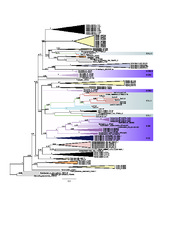
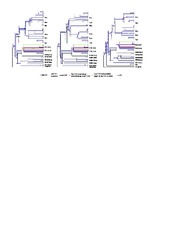
| dc.description.abstract | Background: Calcium carbonate biominerals form often complex and beautiful skeletal elements, including coral exoskeletons and mollusc shells. Although the ability to generate these carbonate structures was apparently gained independently during animal evolution, it sometimes involves the same gene families. One of the best-studied of these gene families comprises the α- carbonic anhydrases (CAs), which catalyse the reversible transformation of CO2 to HCO3 − and fulfill many physiological functions. Among Porifera –the oldest animal phylum with the ability to produce skeletal elements– only the class of calcareous sponges can build calcitic spicules, which are the extracellular products of specialized cells, the sclerocytes. Little is known about the molecular mechanisms of their synthesis, but inhibition studies suggest an essential role of CAs. In order to gain insight into the evolution and function of CAs in biomineralization of a basal metazoan species, we determined the diversity and expression of CAs in the calcareous sponges Sycon ciliatum and Leucosolenia complicata by means of genomic screening, RNA-Seq and RNA in situ hybridization expression analysis. Active biomineralization was located with calcein-staining. Results: We found that the CA repertoires of two calcareous sponge species are strikingly more complex than those of other sponges. By characterizing their expression patterns, we could link two CAs (one intracellular and one extracellular) to the process of calcite spicule formation in both studied species. The extracellular biomineralizing CAs seem to be of paralogous origin, a finding that advises caution against assuming functional conservation of biomineralizing genes based upon orthology assessment alone. Additionally, calcareous sponges possess acatalytic CAs related to human CAs X and XI, suggesting an ancient origin of these proteins. Phylogenetic analyses including CAs from genomes of all non-bilaterian phyla suggest multiple gene losses and duplications and presence of several CAs in the last common ancestor of metazoans. Conclusions: We identified two key biomineralization enzymes from the CA-family in calcareous sponges and propose their possible interaction in spicule formation. The complex evolutionary history of the CA family is driven by frequent gene diversification and losses. These evolutionary patterns likely facilitated the numerous events of independent recruitment of CAs into biomineralization within Metazoa. | en_US |