| dc.contributor.author | Gomes, Ana Silva | eng |
| dc.contributor.author | Kamisaka, Yuko | eng |
| dc.contributor.author | Harboe, Torstein | eng |
| dc.contributor.author | Power, Deborah M. | eng |
| dc.contributor.author | Rønnestad, Ivar | eng |
| dc.date.accessioned | 2014-06-06T12:44:38Z | |
| dc.date.available | 2014-06-06T12:44:38Z | |
| dc.date.issued | 2014-02-19 | eng |
| dc.identifier.issn | 1471-213X | en_US |
| dc.identifier.uri | http://hdl.handle.net/1956/7946 | |
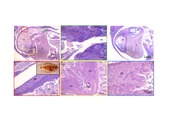
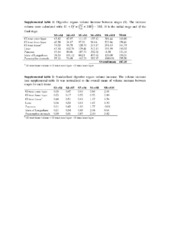
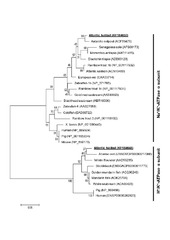
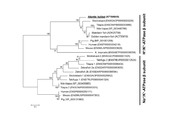
| dc.description.abstract | Background: Flatfish metamorphosis is a hormone regulated post-embryonic developmental event that transforms a symmetric larva into an asymmetric juvenile. In altricial-gastric teleost fish, differentiation of the stomach takes place after the onset of first feeding, and during metamorphosis dramatic molecular and morphological modifications of the gastrointestinal (GI-) tract occur. Here we present the functional ontogeny of the developing GI-tract from an integrative perspective in the pleuronectiforme Atlantic halibut, and test the hypothesis that the multiple functions of the teleost stomach develop synchronously during metamorphosis. Results: Onset of gastric function was determined with several approaches (anatomical, biochemical, molecular and in vivo observations). In vivo pH analysis in the GI-tract lumen combined with quantitative PCR (qPCR) of α and β subunits of the gastric proton pump (H+/K+-ATPase) and pepsinogen A2 indicated that gastric proteolytic capacity is established during the climax of metamorphosis. Transcript abundance of ghrelin, a putative orexigenic signalling molecule produced in the developing stomach, correlated (p < 0.05) with the emergence of gastric proteolytic activity, suggesting that the stomach’s role in appetite regulation occurs simultaneously with the establishment of proteolytic function. A 3D models series of the GI-tract development indicated a functional pyloric sphincter prior to first feeding. Observations of fed larvae in vivo confirmed that stomach reservoir function was established before metamorphosis, and was thus independent of this event. Mechanical breakdown of food and transportation of chyme through the GI-tract was observed in vivo and resulted from phasic and propagating contractions established well before metamorphosis. The number of contractions in the midgut decreased at metamorphic climax synchronously with establishment of the stomach’s proteolytic capacity and its increased peristaltic activity. Putative osmoregulatory competence of the GI-tract, inferred by abundance of Na+/K +-ATPase α transcripts, was already established at the onset of exogenous feeding and was unmodified by metamorphosis. Conclusions: The functional specialization of the GI-tract was not exclusive to metamorphosis, and its osmoregulatory capacity and reservoir function were established before first feeding. Nonetheless, acid production and the proteolytic capacity of the stomach coincided with metamorphic climax, and also marked the onset of the stomach’s involvement in appetite regulation via ghrelin. | en_US |
| dc.language.iso | eng | eng |
| dc.publisher | BioMed Central | en_US |
| dc.relation.ispartof | <a href="http://hdl.handle.net/1956/7974" target="blank">Morphological and functional modifications of the gastrointestinal tract during metamorphosis in Atlantic halibut (Hippoglossus hippoglossus)</a> | en_US |
| dc.rights | Attribution CC BY | eng |
| dc.rights.uri | http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0/ | eng |
| dc.subject | Atlantic halibut | eng |
| dc.subject | Gastric proton pump | eng |
| dc.subject | Gastrointestinal tract | eng |
| dc.subject | Ghrelin | eng |
| dc.subject | Motility | eng |
| dc.subject | Na+/K+-ATPase | eng |
| dc.subject | Pepsinogen | eng |
| dc.subject | Ontogeny | eng |
| dc.subject | pH | eng |
| dc.subject | Stomach | eng |
| dc.title | Functional modifications associated with gastrointestinal tract organogenesis during metamorphosis in Atlantic halibut (Hippoglossus hippoglossus) | en_US |
| dc.type | Peer reviewed | |
| dc.type | Journal article | |
| dc.date.updated | 2014-04-02T10:39:15Z | |
| dc.description.version | Peer Reviewed | |
| dc.description.version | publishedVersion | en_US |
| dc.rights.holder | Ana S Gomes et al.; licensee BioMed Central Ltd. | en_US |
| dc.rights.holder | Copyright 2014 Gomes et al.; licensee BioMed Central Ltd. | en_US |
| dc.source.articlenumber | 11 | |
| dc.identifier.doi | https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-213x-14-11 | |
| dc.identifier.cristin | 1154003 | |
| dc.source.journal | BMC Developmental Biology | |
| dc.source.40 | 14 | |