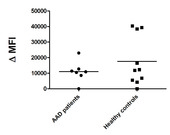
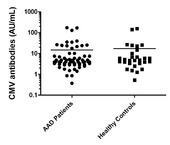
| dc.description.abstract | Background. Autoimmune Addison’s disease (AAD) is caused by multiple genetic and environmental factors. Variants of genes encoding immunologically important proteins such as the HLA molecules are strongly associated with AAD, but any environmental risk factors have yet to be defined. We hypothesized that primary or reactivating infections with cytomegalovirus (CMV) could represent an environmental risk factor in AAD, and that CMV specific CD8+ T cell responses may be dysregulated, possibly leading to a suboptimal control of CMV. In particular, the objective was to assess the HLA-B8 restricted CD8+ T cell response to CMV since this HLA class I variant is a genetic risk factor for AAD. Methods. To examine the CD8+ T cell response in detail, we analyzed the HLA-A2 and HLA-B8 restricted responses in AAD patients and healthy controls seropositive for CMV antibodies using HLA multimer technology, IFN-γ ELISpot and a CD107a based degranulation assay. Results. No differences between patients and controls were found in functions or frequencies of CMV-specific T cells, regardless if the analyses were performed ex vivo or after in vitro stimulation and expansion. However, individual patients showed signs of reactivating CMV infection correlating with poor CD8+ T cell responses to the virus, and a concomitant upregulation of interferon regulated genes in peripheral blood cells. Several recently diagnosed AAD patients also showed serological signs of ongoing primary CMV infection. Conclusions. CMV infection does not appear to be a major environmental risk factor in AAD, but may represent a precipitating factor in individual patients. | en_US |