| dc.contributor.author | Delaleu, Nicolas Hervé | en_US |
| dc.contributor.author | Nguyen, Cuong Q. | en_US |
| dc.contributor.author | Tekle, Kidane Mebrahtu | en_US |
| dc.contributor.author | Jonsson, Roland | en_US |
| dc.contributor.author | Peck, Ammon B. | en_US |
| dc.date.accessioned | 2014-09-16T12:11:53Z | |
| dc.date.available | 2014-09-16T12:11:53Z | |
| dc.date.issued | 2013-10-31 | eng |
| dc.identifier.issn | 1478-6362 | |
| dc.identifier.uri | https://hdl.handle.net/1956/8492 | |
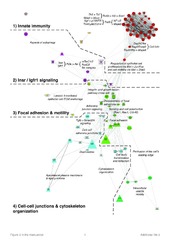
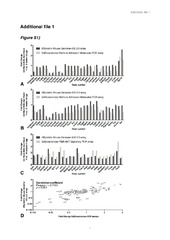
| dc.description.abstract | Introduction: Our understanding of autoimmunity is skewed considerably towards the late stages of overt disease and chronic inflammation. Defining the targeted organ’s role during emergence of autoimmune diseases is, however, critical in order to define their etiology, early and covert disease phases and delineate their molecular basis. Methods: Using Sjögren’s syndrome (SS) as an exemplary rheumatic autoimmune disease and temporal global gene-expression profiling, we systematically mapped the transcriptional landscapes and chronological interrelationships between biological themes involving the salivary glands’ extracellular milieu. The time period studied spans from pre- to subclinical and ultimately to onset of overt disease in a well-defined model of spontaneous SS, the C57BL/6. NOD-Aec1Aec2 strain. In order to answer this aim of great generality, we developed a novel bioinformatics-based approach, which integrates comprehensive data analysis and visualization within interactive networks. The latter are computed by projecting the datasets as a whole on a priori-defined consensus-based knowledge. Results: Applying these methodologies revealed extensive susceptibility loci-dependent aberrations in salivary gland homeostasis and integrity preceding onset of overt disease by a considerable amount of time. These alterations coincided with innate immune responses depending predominantly on genes located outside of the SS-predisposing loci Aec1 and Aec2. Following a period of transcriptional stability, networks mapping the onset of overt SS displayed, in addition to natural killer, T- and B-cell-specific gene patterns, significant reversals of focal adhesion, cell-cell junctions and neurotransmitter receptor-associated alterations that had prior characterized progression from pre- to subclinical disease. Conclusions: This data-driven methodology advances unbiased assessment of global datasets an allowed comprehensive interpretation of complex alterations in biological states. Its application delineated a major involvement of the targeted organ during the emergence of experimental SS. | en_US |
| dc.language.iso | eng | eng |
| dc.publisher | BioMed Central | eng |
| dc.rights | Attribution CC BY | eng |
| dc.rights.uri | http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0 | eng |
| dc.title | Transcriptional landscapes of emerging autoimmunity: transient aberrations in the targeted tissue's extracellular milieu precede immune responses in Sjögren's syndrome | en_US |
| dc.type | Peer reviewed | |
| dc.type | Journal article | |
| dc.date.updated | 2014-04-02T10:41:53Z | |
| dc.description.version | publishedVersion | en_US |
| dc.rights.holder | Copyright 2013 Delaleu et al.; licensee BioMed Central Ltd. | |
| dc.rights.holder | Nicolas Delaleu et al.; licensee BioMed Central Ltd. | |
| dc.source.articlenumber | R174 | |
| dc.identifier.doi | https://doi.org/10.1186/ar4362 | |
| dc.identifier.cristin | 1116169 | |
| dc.source.journal | Arthritis Research & Therapy | |
| dc.source.40 | 15 | |