Ursodeoxycholic Acid Inhibits Glioblastoma Progression via Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Related Apoptosis and Synergizes with the Proteasome Inhibitor Bortezomib
| dc.contributor.author | Yao, Zhong | |
| dc.contributor.author | Zhang, Xun | |
| dc.contributor.author | Zhao, Feihu | |
| dc.contributor.author | Wang, Shuai | |
| dc.contributor.author | Chen, Anjing | |
| dc.contributor.author | Huang, Bin | |
| dc.contributor.author | Wang, Jian | |
| dc.contributor.author | Li, Xingang | |
| dc.date.accessioned | 2021-07-12T11:19:25Z | |
| dc.date.available | 2021-07-12T11:19:25Z | |
| dc.date.created | 2021-01-11T13:10:09Z | |
| dc.date.issued | 2020 | |
| dc.identifier.issn | 1948-7193 | |
| dc.identifier.uri | https://hdl.handle.net/11250/2764158 | |
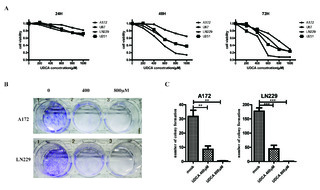
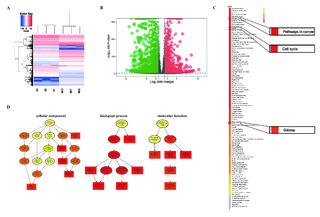
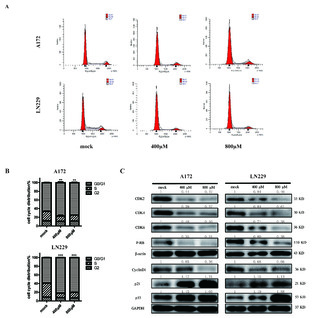
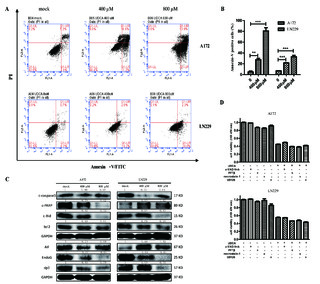
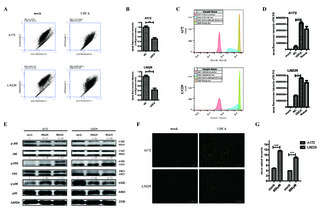
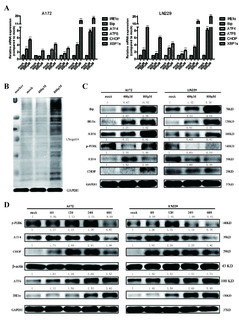
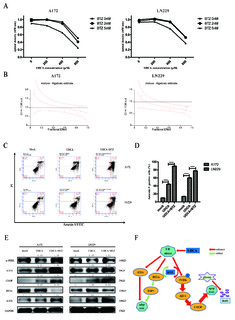
| dc.description.abstract | Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) has demonstrated cancer suppressive potential in several tumors. Here, we investigated the antitumor potential and biochemical mechanism of UDCA on glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), the deadliest form of brain cancer with a median survival of 15 months. Cell viability was assessed using the CCK-8 and colony forming assays. Expression profiles were obtained using RNA sequencing, and PCR and Western blot were used to validate changes in related markers at the RNA and protein levels. Flow cytometry was used to examine cell cycle, apoptosis, mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP), and reactive oxygen species (ROS). UDCA inhibited GBM cell viability in a dose- and time-dependent manner. Flow cytometry demonstrated that cells were arrested in the G1 phase and underwent apoptosis. The RNA sequencing results showed UDCA treatment in part targeted gene expression related to mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum (ER). UDCA indeed led to decreased MMP, overproduction of ROS, and ER stress. Three critical ER stress sensors ATF6, IRE1α, and PERK were increased in the acute phase. Additionally, combining UDCA with the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib (BTZ) achieved a synergistic effect through enhancing the PERK/ATF4/CHOP pathway and protracting ER stress. UDCA inhibited GBM progression, and the combination with BTZ achieved a synergistic effect via protracted ER stress. Thus, UDCA, alone or with combination of BTZ, shows promise as a possible therapeutic agent for the treatment of GBM. | en_US |
| dc.language.iso | eng | en_US |
| dc.publisher | American Chemical Society | en_US |
| dc.title | Ursodeoxycholic Acid Inhibits Glioblastoma Progression via Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Related Apoptosis and Synergizes with the Proteasome Inhibitor Bortezomib | en_US |
| dc.type | Journal article | en_US |
| dc.type | Peer reviewed | en_US |
| dc.description.version | acceptedVersion | en_US |
| dc.rights.holder | Copyright 2020 American Chemical Society | en_US |
| cristin.ispublished | true | |
| cristin.fulltext | postprint | |
| cristin.fulltext | postprint | |
| cristin.fulltext | postprint | |
| cristin.fulltext | postprint | |
| cristin.fulltext | postprint | |
| cristin.fulltext | postprint | |
| cristin.fulltext | postprint | |
| cristin.fulltext | postprint | |
| cristin.qualitycode | 1 | |
| dc.identifier.doi | 10.1021/acschemneuro.0c00095 | |
| dc.identifier.cristin | 1868961 | |
| dc.source.journal | ACS Chemical Neuroscience | en_US |
| dc.source.pagenumber | 1337-1346 | en_US |
| dc.identifier.citation | ACS Chemical Neuroscience. 2020, 11 (9), 1337-1346. | en_US |
| dc.source.volume | 11 | en_US |
| dc.source.issue | 9 | en_US |
Files in this item
This item appears in the following Collection(s)
-
Department of Biomedicine [710]
-
Registrations from Cristin [9791]